Common Problems of Patent Subject Matters in the Field of IT
In the previous article, we introduces the the subject matter problem for patents in China. Simply put, patent subject matters are also referred to as the protecting object of the patent law. If a patent has the problem of subject matter, it means that the invention application is not the object of patent protection. And if a patent has the problem of subject matter, it shall not be granted patent right.
This article focuses on the common problems of patent subject matters in the field of IT.
IT Patent Applications
The technology of the IT field is actually the technology realized by computing systems. The technology may involve hardware as well as software. Generally, invention patents related to software technology are prone to subject matter problems. It should be noted that utility model patents related to technology of computer programs are also prone to subject matter problems. We will talk more about utility patent in detail in other articles later.
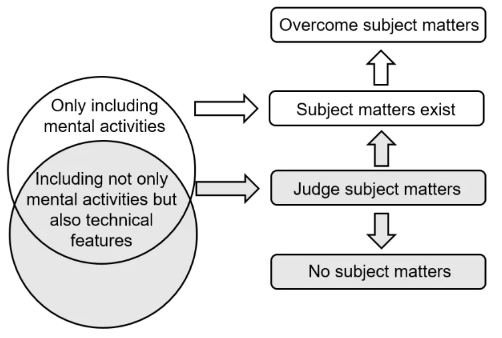
Technology involving software is essentially technology implemented through computer programs. The content executed by a computer program may include mental activities. As stipulated in Article 25.1.2 of the Patent Law, the rules and methods for mental activities shall not be granted patent rights. Therefore, when applying for an invention patent for a technology involving mental activities performed by a computer, it may not be granted patent right because of the subject matter problem.
On the one hand, if the content executed by computer programs only includes mental activities, the application will surely have the subject matter problem, and thus will not be granted patent right. On the other hand, if it includes not only mental activities, but also technical features, whether the application has the problems of subject matter will be evaluated from the perspective that whether it belongs to a technical solution.
Common mental activities related to computer programs
- Algorithms and mathematical computing rules
Algorithms and mathematical computing rules belong to mental activities. If a computer program merely executes algorithms and mathematical computing rules without applying computing means, then it also belongs to mental activities. Therefore, if claims only include algorithms and mathematical calculations, it will face the subject problem.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, the application of machine learning models is becoming more and more extensive. In order to make the model application more in line with the requirements, the training of the model is studied by many IT companies. However, in patent examination, simple model training that is separated from the actual application is easily regarded as a mathematical rule, and may be objected by subject matter problem.
Example (quoted from Guidelines for Patent Examination)
1. A method for establishing a model, comprising:
obtaining a target first model by training an initial first model according to a feature value in at least one first training sample and a feature value in at least one second training sample;
obtaining an extracted feature value corresponding to each training sample by processing the feature value in each first training sample respectively according to the target first model; and
obtaining a target second model by training an initial second model with an extracted training sample formed based on the extracted feature value and a label value corresponding to the each first training sample.
Analysis: The feature value of the processed training sample, the extracted feature value of the processed training sample, the label value of the processed training sample, the first model and the second model are all abstract general data. The processing process of using the relevant data of the training sample to train the mathematical model is a series of abstract mathematical methods. The final result is also an abstract general model, which does not involve the combination with specific application fields, and belongs to the optimization of abstract mathematical methods. Moreover, the entire solution does not include any technical features. Therefore, it does not belong to the subject of patent protection.
- Computer programs
Computer programs consists of codes, which are equivalent to codes based on mental activities and can only be protected by software copyrights.
- Other common mental activities
Rules and methods for games, Chinese character encoding methods, methods of predicting economic trends, etc. Similar to algorithms or mathematical computing rules, rules or methods executed by computer programs are also mental activities.
How to judge whether technical subject matters relating to computer programs exist
As mentioned above, if the content executed by computer programs are all mental activities, the application will inevitably face subject matters. However, if both mental activities and technical features are included, it is complicated to judge whether subject matters exist.
According to Section 2, Chapter 9, Part II of Guidelines for Patent Examination: an invention patent application relating to computer programs is the subject of patent protection only if it constitutes a technical solution. If the solution of an invention application relating to computer programs involves the execution of computer programs not in order to solve technical problems, or does not reflect technical means in conformity with the laws of nature by computer running programs to control and process external or internal objects, or the effect obtained is not restrained by the laws of nature, the solution is not the subject matter of patent protection.
Actually, the above provisions are consistent with the provisions of Article 2, Paragraph 2 of the Patent Law. According to Article 2.2., “invention” in the Patent Law means any new technical solution relating to a product, a process or improvement thereof.
Therefore, if both mental activities and technical means are included, it can be judged whether subject matters exist from the perspective of “technical solution”.
According to Section 2, Chapter 1, Part II of Guidelines for Patent Examination, a technical solution is an aggregation of technical means applying the laws of nature to solve a technical problem. Usually, technical means are embodied as technical features. A solution that does not adopt technical means to solve a technical problem and thereby does not achieve any technical effect in compliance with the laws of nature does not constitute a subject matter as defined in Article 2.2. of the Patent Law. From this it can be seen, an invention application constitutes a technical solution when it uses technical means, solves technical problems and produces technical effect. In other words, technical solutions usually include technical features, but solutions that include technical features are not necessarily technical solutions.
In fact, solutions constituted by mental activities are not technical solutions, and therefore are not the subject matter of patent protection.
Example (quoted from Guidelines for Patent Examination)
1. A method for economic climate index analysis based on regional electricity consumption characteristics, comprising:
selecting preliminary indicators of an economic climate index of an area to be detected according to economic data and electricity consumption data of the area to be detected, wherein the preliminary indicators includes an economic indicator and an electricity consumption indicator;
determining an economic climate indicator system of the area to be detected by executing a cluster analysis method and a time difference correlation analysis method by a computer, wherein the economic climate indicator system includes a leading indicator, a consistent indicator and a lagging indicator; and
obtaining the economic climate index of the area to be detected through a synthetic index calculation method according to the economic climate indicator system of the area to be detected.
Analysis: Although the solution in the example is executed by computers, its processing objects are various economic indicators and electricity consumption indicators. What the solution aims to solve is how to judge the economic trend, and thus does not constitute a technical problem. What it utilizes for analyzing the economic trend is analyzing economic data and electricity consumption and following economic management methods without restriction of the laws of nature, and thus is not technical means. Moreover, the economic climate index obtained for evaluating the economy is not technical effect in conformity with the laws of nature.
Although technical features are included in the solution, the overall solution is not technical solution and therefore are not the subject matter of patent protection.
For judging whether a patent application has subject matters, its principle is the Patent Law, but in practice, it is more based on examples provided in the Guidelines for Patent Examination. It should be noted that because the actual invention applications may not be as clear as examples in the Guidelines for Patent Examination, it is more complicated whether the patent application for invention that contains algorithm features or business rules and method features, and contains technical features has subject matters. Therefore, when applying for a patent, you can try to avoid high-risk areas concerning subject matters. In addition, applicants (attorneys) need to pay attention to writing skills and experience.
How to overcome subject matters in the field of IT
(1) To avoid rules and methods that only fall into mental activities prescribed in Article 25.1.2 of the Patent Law and that do not contain any technical features.
To avoid solutions that only relate to a rule and method for mental activities executed by computer programs, the rule and method of mental activities should be combined with its corresponding technical field to constitute technical solutions. In other words, technical features should be added into solutions.
(2) To fall into technical solutions stipulated in Article 2.2 of the Patent Law, that is, to use technical means to solve technical problems and obtain technical effects.
However, as analyzed above, even if technical features are added, there may still be subject matters. Therefore, in order to overcome subject matters, in addition to adding technical features, it should be taken into consideration technical problems to be solved, technical effects produced and whether it meets requirements of technical solutions.
A patent in the IT field is the subject of patent protection only if it constitutes a technical solution that can be constituted by combining patent claims with specific application scenarios. For example, the solution provided in a patent in the IT filed aims to realize controls on industrial process, measurement or test process and obtain the industrial process control effect in conformity with the laws of nature by executing an industrial process control program through computes and completing controls on the implementation of each stage of the industrial process according to the laws of nature. For another example, the every step involved in the algorithm in claims of a patent in the IT field is closely related to technical problems to be solved. The data processed by the algorithm is the data with exact technical meaning in the technical field. Besides, the execution can embody the process of solving certain technical problem directly by using the laws of nature and produce technical effects. In this case, solutions as defined in these claims, generally, fall into solutions stipulated in Article 2.2 of the Patent Law
For data algorithms, especially model trainings mentioned above, the core of overcoming subject matters lies in the combination with the actual scene.
All in all, in order to avoid subject matters, patent claims in the IT field need to be not only a rule and method for mental activities but a technical solution. Besides, the technical solution needs to include three elements: technical problem, technical means and technical effect.
Example (quoted from Guidelines for Patent Examination):
1. A training method for a convolutional neural network (CNN) model, wherein the method comprises:
obtaining initial model parameters of the CNN model to be trained, wherein the initial model parameters include initial convolution kernels of convolutional layers of all levels, initial bias matrices of the convolutional layers of all levels, an initial weight matrix of a fully connected layer and an initial bias vector of the fully connected layer;
obtaining a plurality of training images;
on the convolutional layers of all levels, obtaining a first feature image of each of the training images on the convolutional layers of all levels by using the initial convolution kernels and the initial bias matrices of the convolutional layers of all levels to perform a convolution operation and a maximal pooling operation on each of the training images, respectively;
obtaining a second feature image of each of the training images on the convolutional layers of all levels by performing a horizontal pooling operation on the first feature image of each of the training images on the convolutional layer of at least one of all the levels;
determining a feature vector of each of the training images according to the second feature image of each of the training images on the convolutional layers of all levels;
obtaining a class probability vector of each of the training images by processing each feature vector according to the initial weight matrix and the initial bias vector;
calculating a class error according to the class probability vector of each of the training images and an initial class of each of the training images;
adjusting the model parameters of the CNN model to be trained based on the class error;
based on the adjusted model parameters and the plurality of the training images, continuing the process of adjusting the model parameter until the number of iterations reaches a preset number; and
determining the model parameters obtained when the number of iterations reaches the preset number as the model parameters of the trained CNN model.
Analysis: Although the technical solution is a model training method, it is clarified that the data processed in each step of the model training method are image data and how to process the image data in each step is also clarified, which shows that the neural network training algorithm is closely related to image information processing. To solve the technical problem that CNN model can only recognize images with a fixed size, the method of processing and training images differently on different convolutional layers is adopted. By using such technical means applying the laws of nature, technical effect is obtained that the trained CNN model can recognize images with any size to be recognized. Therefore, it is patentable subject matter.

